Reliable vehicle detection with radar
TRAFFIC RADAR
Traffic technology
In transport, radar technology boasts a wide variety of applications. Radar is predestined for transport monitoring and has been established for many years as an outstanding technology solution in the traffic sector.
A typical example is police radar traps. However, also more complex applications such as traffic assessment and statistics for intersection management can be achieved using radar-based vehicle detection. New further technical developments in sensors also pave the way for innovative transport concepts for smart cities.
Radar achieves high ranges and measures the following parameters: direction of movement, speed, distance, and angular position of objects or persons. This allows road users to be located. Tracking is also used to determine the movement behaviour of vehicles. These data provide relevant traffic information that contributes to greater safety and efficiency in road traffic.
Rely on more Senses – Take advantage of radar’s benefits for your traffic applications
- anonymous detection of road users
- precise measurement results
- traffic information in real time
- no need for maintenance or cleaning free
- robust measuring technology – suitable for outdoor use
- non-invasive – no interference with infrastructure or disruptions to traffic flow required
Equipped for any traffic situation
Innovative radar sensors from InnoSenT
The range and aperture angle of our radar products are optimally coordinated with the use case in road traffic, and a GUI enables them to be adapted to individual road situations. This facilitates installation and adjustment of the sensors. Our radar-technology-based end products handle a wide variety of tasks, such as displaying speeds in limited-traffic areas, measuring clearance on a multi-lane motorway, vehicle counting and classification, or traffic monitoring in real time at large intersections.
Intersection
Chaos often reigns at rush hour in the main traffic hubs. Traffic jams and congestion are the order of the day. Advanced radar systems provide comprehensive traffic information in real time. In addition to recording the speed and distance of vehicles, this means that road users’ path of movement, for instance, can also be tracked. High-resolution radar systems distinguish the objects precisely even in heavy traffic and enable them to be accurately pinpointed on the lanes. A broad radar beam keeps track of multiple oncoming traffic roads, even at curvy intersections. The radar-based data form the basis for long-term traffic statistics, the planning of traffic concepts and efficient traffic management.
TYPICAL INTERSECTION APPLICATIONS:
- Traffic Light Management
- Stop Bar Detection
- Wrong Way Detection
- Red Light Enforcement
- Traffic Statistics
- Vehicle Classification
- Queue Length Detection
- Advance Detection
- Pedestrian & Bicycle Detection
- Junction Management

Enforcement
This term includes applications for prosecuting traffic-related offences. This task requires top-rate accuracy and reliability. The most common application is the classic police radar trap, for catching speeding drivers. Radar is also used for detecting when drivers run red lights, perform unauthorised turning manoeuvres, or drive the wrong way, or for measuring clearance between cars. In addition, the technology is used for giving drivers constructive feedback: speed displays (‘You are driving … km/h’) or digital traffic displays remind road users to be cautious by performing real-time measurements.
TYPICAL ENFORCEMENT APPLICATIONS:
- Speed Measurement
- Distancemeasurement
- Red Light Enforcement
- Wrong-Way Detection
Arterial
Radar boasts anonymous monitoring of road stretches with multiple lanes. Particularly main thoroughfares and motorways with extremely heavy traffic are equipped with a section-control radar. After all, there is major risk of accidents there. The section control provides information about the traffic situation as well as violations of the applicable regulations, such as speeding. This also applies to monitoring vehicles in tunnels. Radar puts its advantages on full display here: weather and lighting conditions do not impact the performance of the technology. Since the method does not produce any image, it entails no complications with regard to data protection. Also, even if the system is installed subsequently, no changes to the traffic situation are required in its vicinity.
TYPICAL ARTERIAL APPLICATIONS:
- Traffic Flow Analysis
- Traffic Statistics
- Vehicle Classification

Smart City
Growing networking and technological progress are also making cities more intelligent. Radar is thereby becoming increasingly important. Trends such as autonomous driving could not to be made a reality without this technology. In a smart city, sensors and systems help optimise traffic. They also make an important contribution to energy efficiency: radar sensors enable the need-based and automated control of lighting systems as well as parking space monitoring. Radar sensors boast many opportunities for cities: in the future, digital display boards will show important traffic information or warn of dangerous situations.
TYPICAL SMART CITY APPLICATIONS:
- Lightmanagement
- Parking Lot Detection
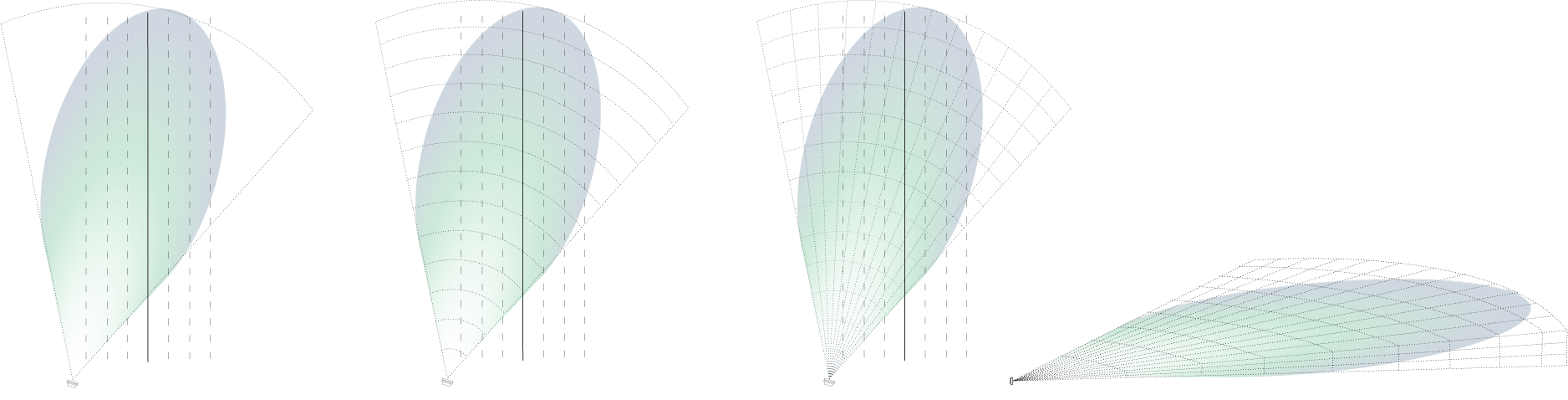
1D-RADAR (CW)
- Seperates vehicles and other road users in only one dimension – velocity
- Measures only one parameter (velocity) and can therefore not localize objects
2D-RADAR (FMCW)
- Seperates vehicles and other road users in two dimensions – velocity and range
- Measures velocity and range and can therefore localize objects in distance to the sensor
3D-RADAR (MIMO)
- Seperates vehicles and other road users in three dimensions – velocity, range and angle
- Measures velocity, range and angle and can therefore localize objects in a 2-dimensional environment
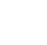
4D-RADAR (MIMO)
- Seperates vehicles and other road users in four dimensions – velocity, range and angle and has additional seperation capabilities in elevation
- Measures velocity, range, angle and elevation angle and can therefore localize objects in a 3-dimensional environment